Array.prototype.at(index);
Array.prototype.at(index); method는 parameter로 반환받고 싶은 element의 index값을 넘겨주며, parameter로 음수와 정수 모두 사용가능하며 음수인 경우 배열의 뒤에서부터 indexing한다.
const array = ["apple", "banana", "lemon"];
console.log(array.at(0)); // "apple"
console.log(array[0]); // "apple"
console.log(array.at(-1)); // "lemon"
console.log(array[array.length -1]); // "lemon"Array.prototype.concat(elements);
Array.prototype.concat(elements); method는 기존 배열에 인자로 들어온 요소나 배열을 합하여 새로운 배열을 반환하는 메서드이다.
- 기존 배열을 변경하지 않는다.
- 인자가 추가된 새로운 배열을 반환한다.
const array = ["apple", "samsung"];
const array2 = ["LG"];
console.log(array.concat(array2)); // [ "apple", "samsung", "LG" ]
console.log(array); // ["apple", "samsung"]
const array3 = array.concat(array2);
console.log(array3); // ["apple", "samsung", "LG"]
Array.prototype.copyWithin(target, start [,end]);
Array.prototype.copyWithin(target, start [,end]); method는 배열의 일부를 얕게 복사한 뒤, 동일한 배열의 다른 위치에 덮은 후 해당 배열을 반환한다. 이때 배열의 길이는 변경되지 않는다.
const array = ['a','b','c','d','e','f'];
const array2 = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g'];
array.copyWithin(2,5); // ['a','b','f','d','e','f']
array2.copyWithin(1,2,5); // ['a','c','d','e','e','f','g']
console.log(array); // ['a','b','f','d','e','f']
console.log(array2); // ['a','c','d','e','e','f','g']Array.prototype.entries()
Array.prototype.entries(); method는 배열의 각 인덱스에 대한 키/값 쌍을 가지는 새로운 Array Iterator 객체를 반환한다.
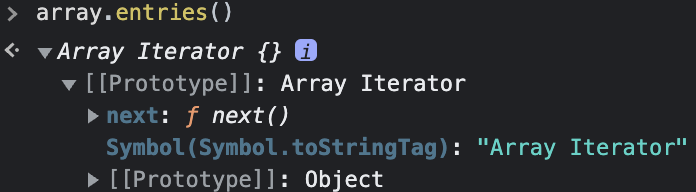
const array = ["apple", "lemon", "orange", "strawberry"];
const iterator = array.entries();
console.log(iterator.next().value)); // [0, "apple"] => Array
console.log(iterator.next().value)); // [1, "lemon"] => Array
console.log(iterator.next().value)); // [2, "orange"] => Array
console.log(iterator.next().value)); // [3, "strawberry"] => Array
console.log(iterator.next().value)); // undefined
Array.prototype.every(function)
Array.prototype.every(function) method는 배열의 모든 요소가 주어진 판별함수를 통과하는지 테스트하는 메서드로, 반환값은 boolean이다.
const isTenOver = (element) => element > 10;
const array = [11,12,14,20];
array.every(isTenOver); // true
Array.prototype.fill(value [, start [ , end] ] );
Array.prototype.fill() method는 배열의 시작부터 끝 이전까지 정적인 값 하나로 모두 채우는 메서드이다.
* parameter
- value : 배열을 채울 값
- start : 시작 인덱스 기본값 0
- end : 끝 인덱스 기본값 array.length
const array = [1,2,3,4,5];
array.fill(5);
console.log(array); // [5,5,5,5,5]
array.fill('a',2,4); // [5,5,'a','a',5]
Array.prototype.filter( callback(element [ , index [ , array ] ] ) [ , thisArg ]);
Array.prototype.filter() 메서드는 매개변수로 주어진 callback 함수의 테스트를 통과한 요소들만 모아 새로운 배열을 반환한다.
- callback : true 를 반환하면 요소를 유지 false를 반환하면 요소를 버린다.
- element : 현재 처리할 요소
- index : 현재 처리할 요소의 인덱스
- array : filter를 호출한 배열
- thisArg : callback을 실행할 때 this로 사용하는 값
const number = [1,2,3,"4",5,6];
const newNumber = number.filter( (element) => typeof element === "number" );
console.log(newNumber); // [1,2,3,5,6]
Array.prototype.find( callback [ , thisArg ] )
Array.prototype.find() 메서드는 주어진 판별함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 값을 반환한다. 해당하는 요소가 없다면 undefined를 반환한다.
const array = ["a",3,4,"b"];
const found = array.find((element) => typeof element === "number");
console.log(found); // 3
const fruits = [
{ name : "banana", quantity : 3 },
{ name : "apple", quantity : 5 },
{ name : "lemon", quantity : 2 }
];
function findApple(fruit){
return fruit.name === "apple";
}
const Apple = fruits.find(findApple);
console.log(Apple); // {name: 'apple', quantity: 5}
Array.prototype.findIndex( callback(element [ , index [ , array ] ]) [ , thisArg ] );
Array.prototype.findIndex() 메서드는 주어진 판별함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 인덱스를 반환한다. 배열의 첫 번째 요소가 존재하지 않는다면 -1을 반환한다.
const fruits = [
{ name : "banana", quantity : 3 },
{ name : "apple", quantity : 5 },
{ name : "lemon", quantity : 2 }
];
function findApple(fruit){
return fruit.name === "apple";
}
function findCherry(fruit){
return fruit.name === "cherry";
}
const Apple = fruits.findIndex(findApple);
console.log(Apple); // 1
const Cherry = fruits.findIndex(findCherry);
console.log(Cherry); // -1
Array.prototype.forEach(callback(currentValue [ , index [ , array ]] ) [ , thisArg ] );
Array.prototype.forEach(); method는 주어진 함수를 배열 요소 각각에 대해 실행한다.
const array = ["apple", "banana", "lemon", "cherry"];
array.forEach( fruit => console.log(fruit) );
// "apple"
// "banana"
// "lemon"
// "cherry"
Array.prototype.includes(valueToFind [, fromIndex ]);
Array.prototype.includes(); method는 배열이 특정 요소를 포함하고 있는지를 판별한다. 반환값은 boolean이다.
- valueToFind : 찾고자하는 요소
- fromIndex : 검색을 시작할 위치
const array = ["apple", "banana", "lemon"];
array.includes("apple"); // true
array.includes("cherry"); // false
array.includes("apple",0); // true
array.includes("apple",2); // false
array.includes("lemon",1); // true
Array.prototype.indexOf(searchElement [, fromIndex])
Array.prototype.indexOf(element, [fromIndex]); 메서드는 배열에서 지정된 요소를 찾을 수 있는 첫 번재 인덱스를 반환하고 존재하지 않으면 -1을 반환한다.
const array = [ "a", "b", "c", "d", "e" ];
console.log( array.indexOf("e") ); // 4
console.log( array.indexOf("f") ); // -1
console.log( array.indexOf("a",2) ); // -1
Array.isArray(obj);
Array.isArray() 메서드는 메서드의 인자가 Array인지 아닌지를 판별한다. 반환값은 Boolean이다.
const array = [1,2,3];
Array.isArray(array); // true
Array.isArray(3); // false[ + ] 계속 추가할 예정
Array.prototype.join()
Array.prototype.map()
...
push()
pop()
reduce()
reverse()
shift()
slice()
some()
sort()
unshift()
toString()
values()
'Language > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ VanillaJS ] Create Tooltip Input Component using VanillaJS (0) | 2022.10.12 |
|---|---|
| [ Javascript ] setTimeout, setInterval (0) | 2022.07.27 |
| [ Javascript ] async/await (0) | 2022.03.07 |
| [ Javascript ] Promise (0) | 2022.03.06 |
| [ Javascript ] Class { ES6 (ES2015) } (0) | 2022.02.20 |